The Importance of a Problem List
The new book K3: A New Problem List in Low-Dimensional Topology grew out of a 2023 AIM workshop designed to create the next version of the famous "Kirby problem lists." Organizers hope that this list, like the previous two, will inspire graduate students and experienced researchers alike, and that it will set the research agenda for the field for the next decade or more.


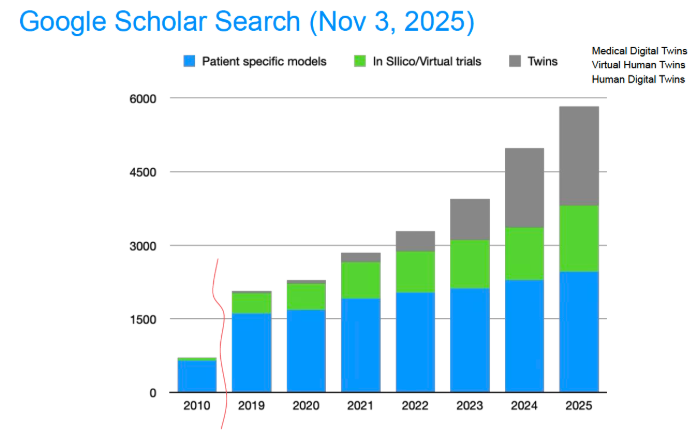
Digital Twins and Personalized Medicine
Digital twins are virtual, data-driven models that replicate physical systems and processes, enabling continuous simulation, prediction, and optimization. In health care, a digital twin of a patient leverages real-time clinical data and computational models to reflect physiology and disease dynamics—allowing clinicians to tailor treatments, manage disease, and enhance outcomes with unprecedented precision.

Homogeneous Dynamics Proof Opens New Doors in Number Theory
A team of mathematicians at the Institute for Advanced Study has released a breakthrough proof that sheds new light on one of number theory’s oldest and most established inquiries. Their achievement highlights the power of a surprising partnership: number theory and dynamical systems.

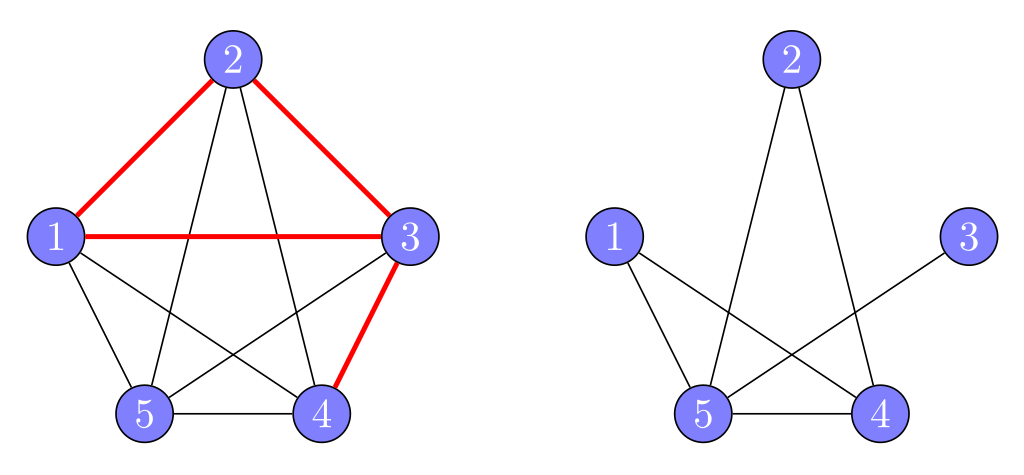
Effective Computation With Hourglass Plabic Graphs
Many students believe they should always expand their algebraic expressions. Yet computations are often easier if we don’t expand too early and instead remember the meaning of fragments of complex expressions. Consider the calculation of the determinant. The classic expansion formula has n! terms and is impractical beyond toy examples. But if we, for instance, spot linear dependence, we can immediately conclude the n! terms will all cancel without actually doing any laborious, error-prone arithmetic.
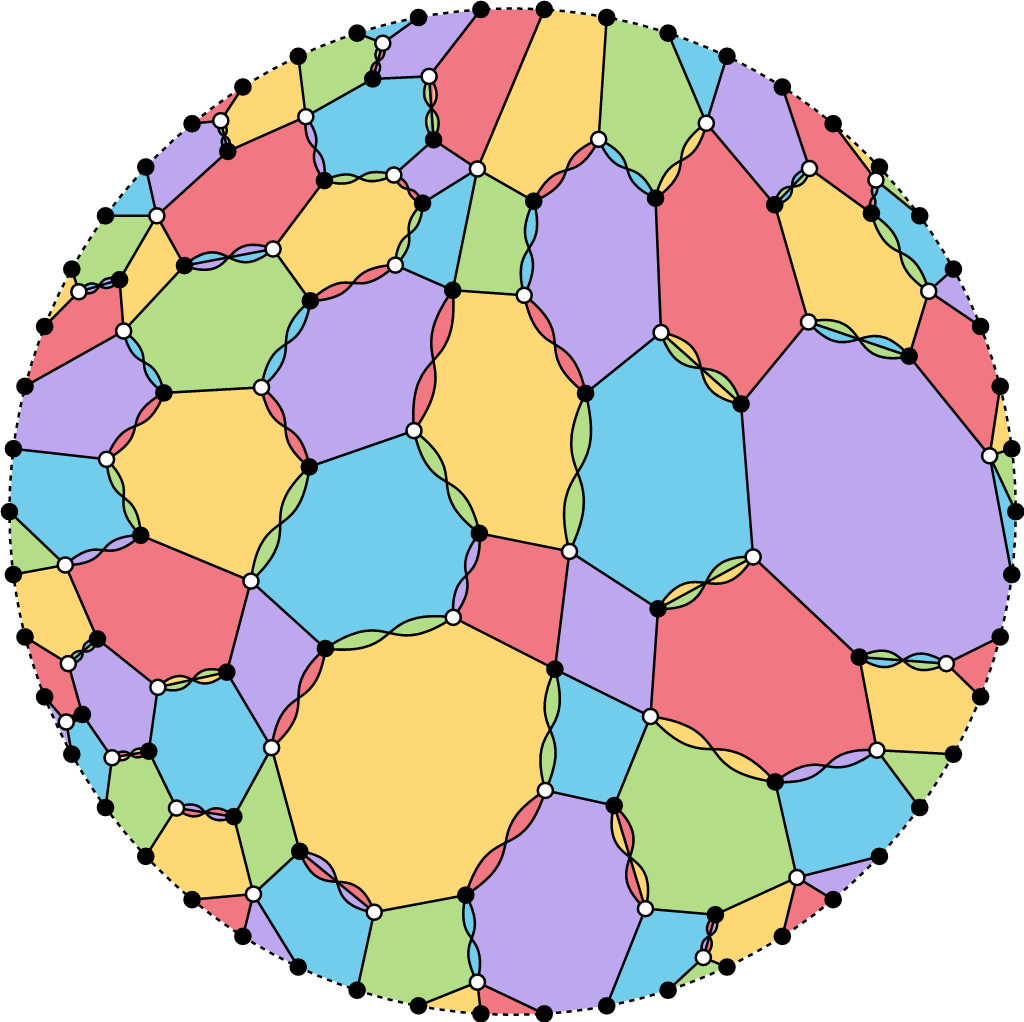

Rigidity and Flexibility in Geometric Constraint Systems
Geometric constraint systems (GCS) are used to model a wide range of geometric objects. These structures come with natural constraints, such as distances, angles, coplanarity, volume, or tangency, that are invariant under Euclidean isometries, namely translations, rotations, and reflections. GCS arise in numerous applications, including structural engineering, crystallography, soft-matter physics, and biochemistry. Two particularly important properties associated with GCS are rigidity and flexibility.
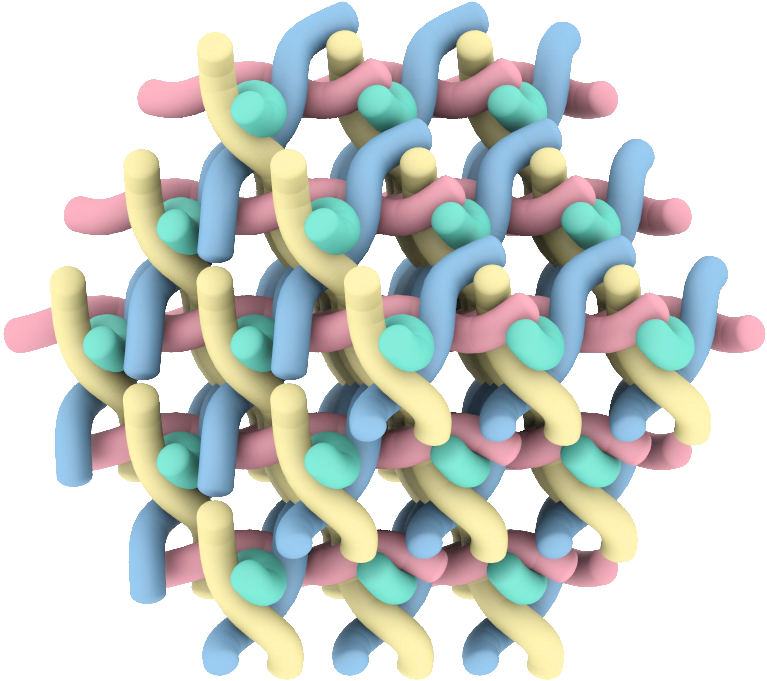

A Massive hypercube hidden in the Bruhat Order, Found by AI
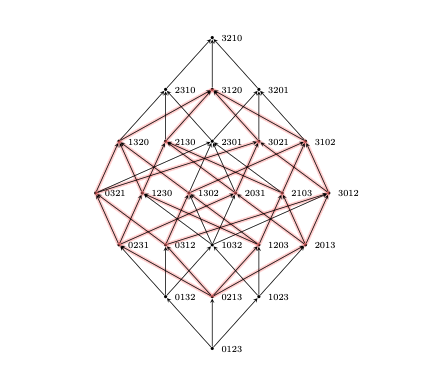
Imagine all possible ways of shuffling numbered cards. Mathematicians organize this enormous set of permutations using a structure called the Bruhat order, which arranges them by declaring τ <σ when a single swap turns τ into σ and increases the deck’s “disorder” in a precise way. This deceptively simple rule has deep consequences in representation theory, geometry, and combinatorics. Within this highly intricate structure, the authors of Bruhat intervals that are large hypercubes [Ell+25] uncover something exceptionally rigid: a gigantic, perfectly organized hypercube hidden inside the seemingly “chaotic” Bruhat order.

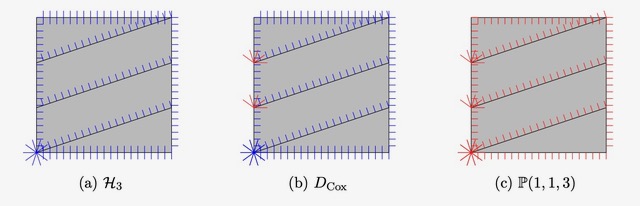
Le roi est mort, vive le roi! (King’s Conjecture and the Cox category)
One question at the heart of two recent AIM workshops, “Syzygies and Mirror Symmetry” in Fall 2023 and "Homological mirror symmetry and multigraded commutative algebra” in Fall 2025, is how the classical algebra-geometry correspondence between graded algebra over a polynomial ring and the geometry of projective space differs when one endows the polynomial ring with the extra structure of a multigrading.

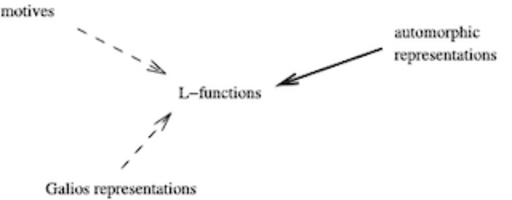
Geometry of Shimura varieties and arithmetic applications to L-functions
Raphaël Beuzart-Plessis, Yifeng Liu, Yichao Tian, Liang Xiao, Wei Zhang, and Xinwen Zhu have published two papers making significant progress on two major conjectures in arithmetic geometry: "Isolation of the cuspidal spectrum, with applications to the Gan-Gross-Prasad conjecture" by Beuzart-Plessis, Liu, Zhang, and Zhu, published in the Annals of Mathematics in 2021; and "On the Beilenson-Bloch-Kato conjecture for Rankin-Selberg motives" by Liu, Tian, Xiao, Zhang, and Zhu, published in Inventiones in 2022. The work originated in the AIM SQuaRE "Geometry of Shimura varieties and arithmetic application to L-functions" which met three times from 2017-2019.

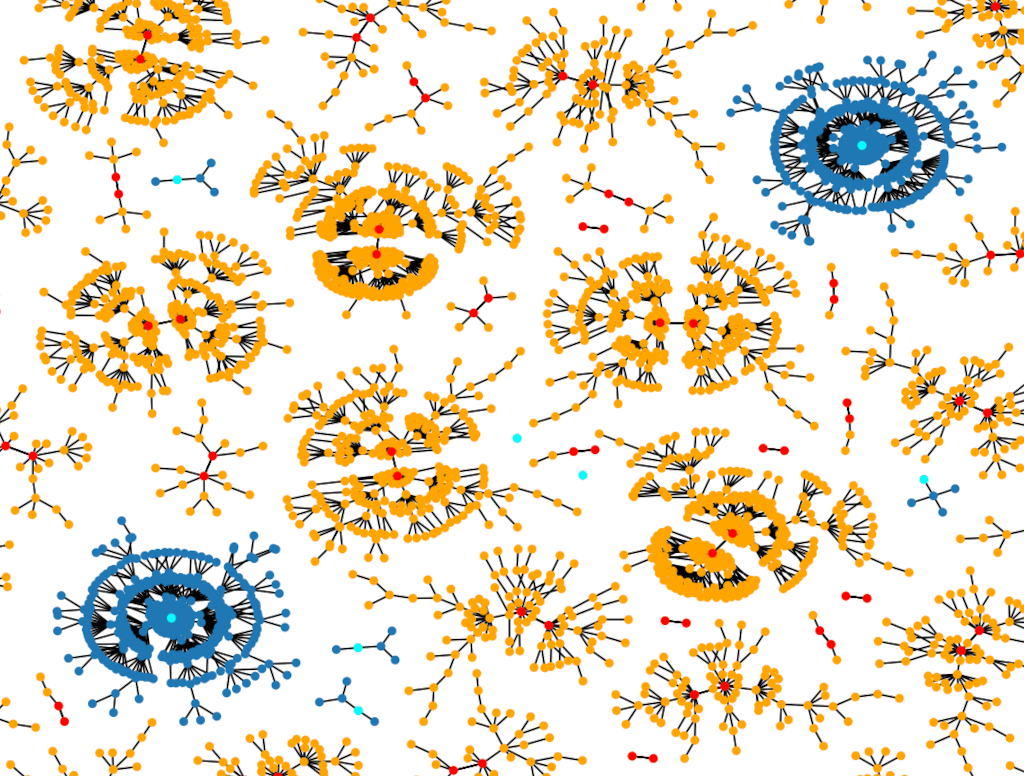
A Breakthrough in Global Dynamics on Graphs
A random network is a mathematical model used to study systems wherein interconnections form by chance. Nodes represent objects or entities; edges represent interactions.

Percolation on Growing Graphs with Infinite-order Phase Transitions
Water percolates through sandstone. Coffee percolates to achieve a bold, strong brew. Ideas percolate over time.